How do RFID labels work?
RFID tags can be compared to a tracking system dedicated to identifying items. For this purpose, a smart tag is used that is similar to a barcode. The abbreviation "RFID" stands for "Radio Frequency Identification". The RFID stickers therefore make use of radio frequency to read out and transfer data.
The data acquisition and transfer takes place between the RFID labels and a reader. Afterwards, the information is forwarded to an RFID computer programme. RFID labels use an antenna and a microchip to ensure that this data transfer runs smoothly.
An RFID transponder is located on the object itself. When the reader emits a signal, it is intercepted by the antenna on the RFID transponder. The signal is then transmitted to the microchip of the transponder and adapted and the modified information is transferred to the reader.
This process may seem complicated at first glance, but in fact the data transfer takes place in a few milliseconds.
Advantages of RFID labels
RFID solutions support companies in their daily work and contribute to the optimisation of everyday business in countless areas. While the barcode scanner has to make visual contact with the label, the data capture and transmission of RFID tags is completely contactless. The transmission of information between the reader and the transponder works by means of radio waves. Accordingly, companies save time and have the possibility to quickly and securely record even inaccessible parts.
Furthermore, the reading of the RFID chips is not affected by external circumstances. Neither dirt, high temperature fluctuations, poor lighting conditions nor moisture have a negative effect on the readability of the data. In fact, the first-read rate of RFID tags is up to 100 percent. It is also possible to decode even faulty tags with special systems.
Furthermore, RFID readers are able to read several tags simultaneously. This bulk reading speeds up data transfer and even entire transport containers can be scanned in a fraction of a second. Nevertheless, the solution is protected against manipulation. This is because the data is not written in plain text, but transmitted in encrypted form to prevent theft.
The RFID applications further ensure a transparent exchange of information in real time, which improves warehouse, inventory and logistics management. Finally, the flow of goods can be controlled, the position of items on delivery can be determined and even food and feed can be traced in accordance with EU Regulation 178/2002.
RFID transponders are almost invisible and can be easily integrated into a wide range of tags. Moreover, the RFID tags are reusable and can be adapted or supplemented at a later date.
Frequency ranges of RFID tags
- Low frequency (LF)/long wave: 125-134 kHz
- High frequency (HF)/short wave: 13.56 MHz
- Ultra high frequency (UHF): 865-869 MHz (European frequencies)
Different RFID tags
Two main types of RFID tags can be distinguished: The active and passive RFID labels.
Active RFID label
The active RFID tag uses either 433 MHz or 915 MHz to transfer data. It is composed of the tag, the antenna and an interrogator. Unlike the passive tag, the active tag is battery operated. This lasts between three and five years and determines the lifespan of the device.
Furthermore, RFID tags can be divided into beacons and transponders. Beacons emit signals every second that can be received over several hundred metres. For this reason, the battery power wears out earlier than with transponders. These are supported by a reader and have a much longer battery life than beacons.
Passive RFID tag
The passive RFID tag communicates on all three frequencies. A distinction is made between inlays and hard tags. The two types differ mainly in the material. Inlays are wafer-thin and can be applied to any material. Hard tags are made of plastic or metal.
Passive RFID labels do not rely on any energy supply, as they feed their power from the electromagnetic signals of the readers. Their reading range is accordingly extremely limited.
Read-only labels
Furthermore, in addition to passive and active RFID tags, there are also special tags. On the one hand, there are tags that can only be read. They cannot be changed, which is why this is the most cost-effective solution.
Tags for simple writing and multiple read-outs
On the other hand, another type of label has been produced to allow easy writing and multiple reading. However, the chips can only be overwritten once.
Rewritable labels
The last form are labels that can be read out unlimitedly as well as rewritten. They are very expensive.
Materials for RFID labels
In addition to the conventional materials for RFID labels, special materials can also be used. These are mainly used for extreme applications. For example, it is no longer a problem to establish contact between the transponder and the reader at very high temperatures. This guarantees identification of the goods at any time throughout the entire production cycle.
Transponders developed for the high-temperature range can withstand temperatures of up to 200 degrees Celsius, which is why metal products can now also be labelled.
Important criteria for the choice of an RFID label
- Material: matched to the surface to be labelled
- Readability: logo, text, serial numbers are perfectly identifiable
- Equipment: optional transmitter for receiving and recording relevant data
- Inlay: high performance RFID antenna matched to the specific application
- Adhesive: high quality material for long lasting adhesion
- Label carrier material: high quality design for professional presentation
Possible applications of RFID labels
RFID labels can be used in countless fields. For example, the tags are used for production control. During industrial production, the tags contribute to documenting the actual state of products. The construction status and the steps taken can be traced by means of RFID chips.
In addition, it is possible to carry out an inventory. Libraries, for example, use RFID technology to check information about the borrowing, return and location of books and other media. But the tags also prove useful in the warehouse. At goods receipt, automatic recording takes place, which is booked in the merchandise management system and ensures that the products are placed in the defined shelf location.
In the free market economy, supply chains are very long and it can be difficult to trace goods. The RFID tag makes this task easier. Information relevant to production and origin is stored on the chip to provide more transparency.
Some companies use RFID tags to distinguish their products from counterfeits. During an authenticity check, RFID technology can distinguish originals from cheap copies. The applications are also used for access control. Authorisations can be checked quickly and easily at entrance areas of authorities, events, airports or shops.
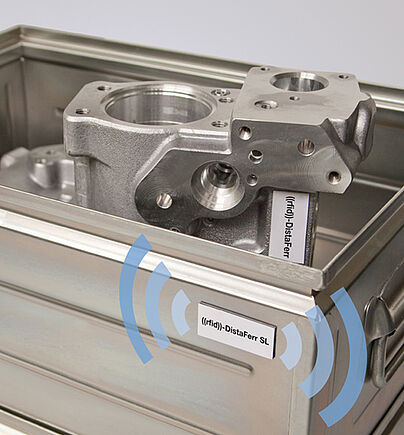
Schreiner Group DistaFerr SL2
When conventional RFID transponders are applied directly to metal this typically produces no or only poor reading results. Since the ((rfid))-DistaFerr SL2 label is not affected by metallic substrates, it can be read from a range of up to four meters on metals. The use of special materials makes the RFID transponder very durable. The ((rfid))-DistaFerr SL2 has been tested to current automotive standards. In addition, it is weatherproof, which makes it suitable for outdoor use. On-site programming and printing (with thermal transfer printers) ensure flexibility of use of the labels.Confidex Steelwave Flex
Flexible on-metal label with extremely strong adhesive. Due to unique more flexible structure compared to other on-metal labels in the market Steelwave Flex is optimal solution to tag small components and assets. Flex is optimized for metal surfaces but do work also on plastics and liquid containers. Steelwave Flex comes with VDA encoding scheme compliant IC by default.Confidex eKanban GTL
eKanban GTL is a master label designed for Global Transport Label (GTL) applications. It is a plug-in label for transport packaging units or plastic load carriers. It is also compliant with VDA recommendations 4994 and 5501.Confidex eKanban SLC
eKanban SLC is a single label designed for Small Load Carrier (SLC) applications. It is a plug-in label for plastic and ESD load carriers. It also complies with VDA recommendations 4994 and 5501.Smartrac Miniweb
Smartrac’s MINIWEB inlays and tags are designed for global retail, industry and supply-chain applications, offering excellent performance on difficult-to-tag or low-detuning materials such as cardboard and plastic, and in other demanding, close-coupling environments.Confidex Carrier Pro
Confidex Carrier family is designed especially for plastic returnable transit item (RTI) tracking. All products can withstand washing processes while maintaining their strong grip on plastic surfaces. Labels can be printed and encoded with standard RFID printers or be ordered pre-personalized. The Carrier PRO offers a large area for visual printing. Unique antenna design offers reliable tracking even when close to products that have high water content.
Didn't find your product?
We deliver thousands of items and only show case a few selected products for given categories.
We are happy to help you find your specific product and can create you a quotation.